What's the difference between a cryptocurrency like Bitcoin and fiat money?
Cryptocurrencies share many similarities with conventional fiat money, but also offer some interesting advantages.
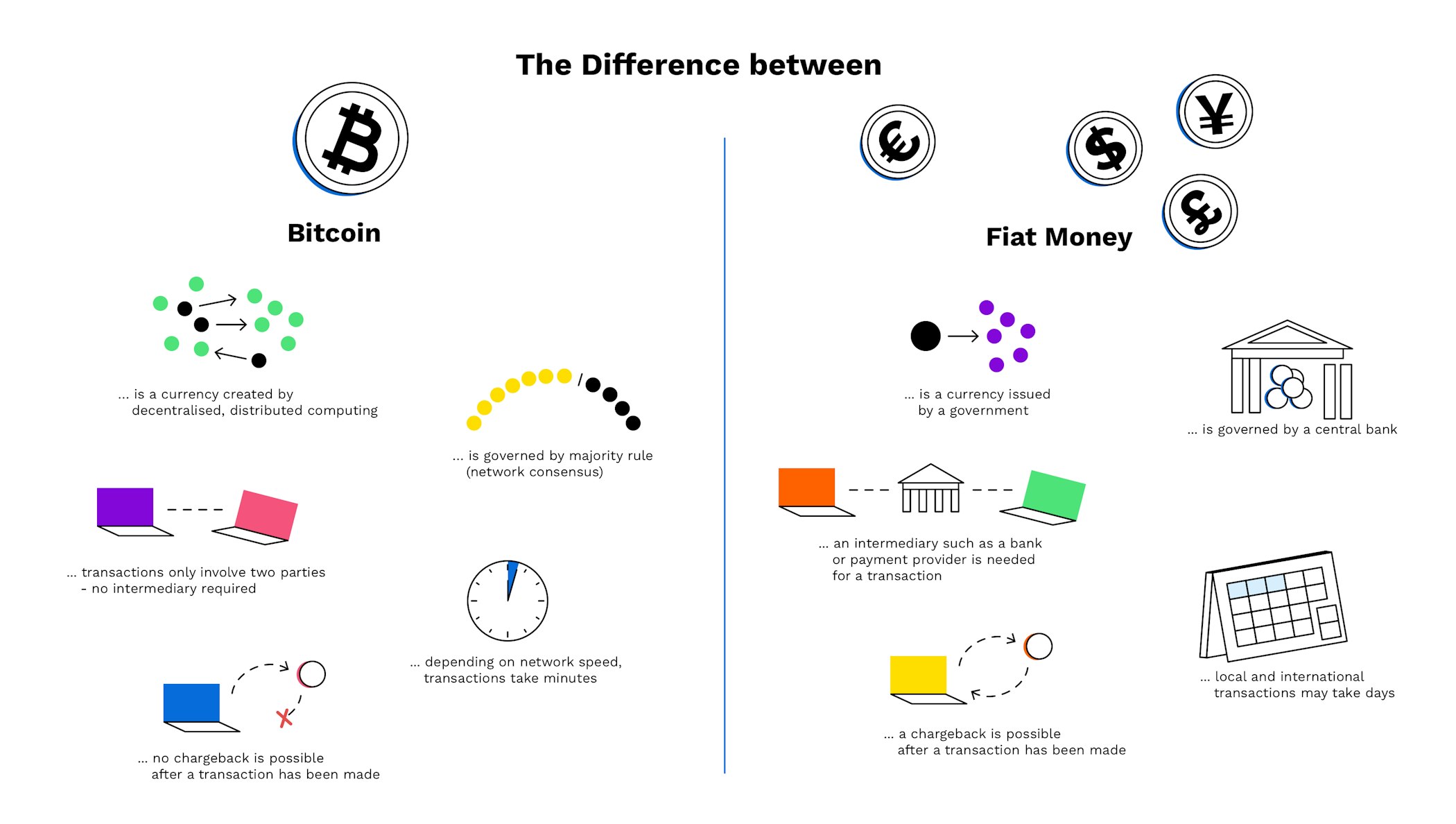
Both can be used for payments and as a store of value
Both rely on widespread consumer trust in order to function as a means of exchange
Fiat money is issued and controlled by (central) banks and governments
Bitcoin is produced and distributed through a process called mining and is not controlled by a centralised authority
Bitcoin can be trusted because it is tamper-proof and cannot be spent twice
A Bitcoin transaction cannot be reversed, cancelled or charged back.
In this article, you will learn the difference between cryptocurrencies and fiat money.
New to Bitpanda? Get started today!
Sign up hereCryptocurrencies and conventional currencies have two essential features: they enable frictionless payments between two parties and act as a store of value.
While trust vested in fiat currencies is ensured through the money supply issued by a central authority, the trust vested in cryptocurrencies is founded on the underlying technology - blockchain technology.
When you buy something with fiat currency, you need to rely on a trustworthy authority such as the European Central Bank (ECB) or governmental institution to serve as an intermediary that vouches for the currency’s worth.
Either way, buyer and seller trust that the currency will still sustain its value after a transaction.
What is fiat money?
Commodity money gets its value from its own worth, like with precious metals (e.g. gold and silver), salt, or even shells. Fiat money has attributed value because a government declares it legal tender - it has no intrinsic value. We can’t talk about fiat money without also discussing inflation . This term inflation refers to the rise in the general price level of goods and services over time, leading to a decrease in the purchasing power of money. Interest rates –relate to the cost of borrowing money or the return on savings and are another important factor in the world of fiat money. Central banks keep adjusting these rates to influence economic activity.
Taking all these factors into account and finding a way to balance them is what monetary policy strives to do. This involves central banks managing money supply and interest rates to control inflation and promote economic stability. They can raise rates to combat inflation or lower them to stimulate borrowing and spending during economic downturns. This, in turn, affects borrowing costs, investment, and overall economic health. Balancing these factors is absolutely essential for a stable economy.
The role of central banks
Central banks play a crucial role in the issuance and management of fiat money within a country's monetary system. Their responsibilities include:
Currency issuance: Central banks are typically the sole authority responsible for issuing physical currency, such as banknotes and coins. They ensure the quality, security, and quantity of these notes and coins in circulation.
Monetary policy: Central banks have the authority to formulate and implement monetary policy. They use various tools to influence the money supply, interest rates, and the overall financial stability of the economy. One primary objective of monetary policy is to control inflation and maintain price stability.
Lender of last resort: Central banks serve as lenders of last resort during financial crises. When commercial banks face liquidity problems and are unable to meet their short-term obligations, central banks provide them with loans or liquidity support to prevent a systemic banking collapse.
Bank supervision and regulation: Central banks often oversee and regulate the banking industry within their jurisdiction. They establish rules and regulations to ensure the safety and soundness of banks, protect depositors, and maintain the stability of the financial system.
Foreign exchange management: Central banks manage a country's foreign exchange reserves, which are holdings of foreign currencies and assets. These reserves are used to stabilize exchange rates, intervene in currency markets, and support the country's international trade and financial transactions.
Interest rate control: Central banks have the authority to set benchmark interest rates, such as the federal funds rate in the United States. Changes in these rates can influence borrowing costs for individuals, businesses, and financial institutions, thereby affecting economic activity and inflation.
Open market operations: Central banks conduct open market operations, which involve buying or selling government securities (bonds) in the open market. These operations affect the money supply and short-term interest rates, allowing central banks to implement monetary policy.
Financial system stability: Central banks monitor and assess the overall stability of the financial system. They identify potential risks and take measures to prevent or mitigate financial crises.
Payment system oversight: Central banks oversee and maintain the efficiency and security of payment systems, ensuring that transactions among banks, businesses, and individuals are smooth and secure.
Currency reserves: Central banks hold foreign currency reserves to facilitate international trade, manage exchange rate fluctuations, and maintain the country's economic stability.
In summary, central banks are the cornerstone of a country's monetary and financial system. They are responsible for controlling the money supply, regulating banks, ensuring economic stability, and playing a vital role in the overall health of the economy. Their actions and policies have far-reaching effects on interest rates, inflation, and the overall well-being of a nation's economy.
Commodity money vs. fiat money
The main difference between commodity money and fiat money lies in their intrinsic value. Commodity money has inherent value because it represents a tangible asset, while fiat money's value is based on trust in the issuing authority. Modern economies predominantly use fiat paper money because it offers greater flexibility and ease of use, but it also requires responsible management by central banks to maintain stability and prevent excessive inflation.
Stablecoins – The intersection of cryptocurrencies and fiat money
Stablecoins are digital currencies designed to maintain a stable value by pegging them to a specific fiat currency, such as the US Dollar (USD) or the Euro (EUR). They provide the benefits of cryptocurrencies, like fast and borderless transactions, while reducing price volatility. These stablecoins are typically backed by reserves of the fiat currency they're pegged to, and their value remains close to 1:1 with that currency, making them a reliable medium of exchange and a store of value in the world of digital finance.
What are cryptocurrencies?
Cryptocurrencies are digital assets that are a medium of exchange between two parties. They allow direct transactions between individuals without the intervention of an intermediary, such as a bank. While fiat money is subject to inflation and central banks can print more at any time, the leading cryptocurrency Bitcoin has a fixed supply of 21.000.000 units, making it even scarcer than gold.
Are cryptocurrencies regulated?
Crypto regulation varies from country to country and is constantly evolving. Some countries have embraced cryptocurrencies and have established clear regulatory frameworks, while others have imposed strict restrictions or bans and only trust
Regulation of cryptocurrencies typically focuses on areas such as:
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements: Many countries require cryptocurrency exchanges and service providers to implement AML and KYC procedures to prevent illicit activities such as money laundering and terrorism financing.
Licensing and registration: Some jurisdictions require cryptocurrency businesses to obtain licenses or register with regulatory authorities to operate legally.
Taxation: Cryptocurrency transactions may be subject to taxation, including capital gains tax, income tax, or value-added tax (VAT), depending on the country's tax laws.
Consumer protection: Regulations often aim to protect consumers by ensuring transparency, security, and fair practices within the cryptocurrency industry.
Securities regulations: In some cases, cryptocurrencies and initial coin offerings (ICOs) may be subject to securities regulations if they are deemed to be securities or investment products.
Financial market oversight: Regulators may monitor cryptocurrency exchanges and trading platforms to prevent fraud, market manipulation, and unfair practices.
Payment services regulations: Some countries classify cryptocurrencies as payment instruments and subject them to specific regulations governing payment services.
Blockchain and smart contract regulations: Some jurisdictions are exploring regulations specific to blockchain technology and smart contracts to promote innovation while addressing legal and compliance concerns.
It's important to note that the regulatory environment for cryptocurrencies is still evolving, and new regulations may be introduced or amended in response to market developments and evolving risks. Cryptocurrency users and businesses should be aware of and comply with the regulations applicable in their jurisdiction to avoid legal issues and ensure their activities are conducted in a compliant manner. So make sure you keep yourself informed at all times.
Are cryptocurrencies and fiat money the same?
Yes and no.
Cryptocurrencies are money insofar as they allow exchanges between two parties and act as a store of value. However, they also offer features which the traditional money system is unable to offer right now: cryptocurrencies can be spent and received by anyone, anywhere, at any time throughout the world and without the need for a bank or a government. This is the most revolutionary aspect of cryptocurrencies.
Furthermore, fiat money basically equates to debt. When a central bank issues banknotes, it is simultaneously issuing you, the consumer, a percentage of your government’s debt. How is this the case, you might ask? Think about how, for example, the EU and the United States create money.
Fiat money has attributed value because a government declares it legal tender - it has no intrinsic value.
Most of the money a government creates is when loans are taken out. Banks create money when people borrow money. Take the case of the US dollar: if no loans were taken out, there likely wouldn’t be any dollars in circulation either. In other words, without consumers taking out debt to banks, the US dollar wouldn’t be out there in the world.
While fiat money seems to get a major part of its value from debt, this is not the case with Bitcoin. Bitcoin has intrinsic value beyond the trust of its community. Bitcoin doesn’t lean on a system of debts, its value boils down to how effective it is as a medium of exchange.
Bitcoin distinguishes itself from fiat currencies through mechanisms like the Bitcoin halving that controls its inflation. This event, occurring approximately every four years, halves the reward for mining new Bitcoin blocks. This reduction in new Bitcoin creation mimics the scarcity of precious metals, potentially increasing Bitcoin's value as its supply diminishes.
For investors, understanding the timing of these events is vital. Our Bitcoin halving countdown provides a definitive exploration of the upcoming halving, giving investors additional context when making important decisions ahead of this market-influencing event.
Cryptocurrencies can be spent and received by anyone, anywhere, and at any time without the need for a bank or a government. This is what makes them so revolutionary.
Bitcoin has created a new form of trust for our future global monetary system. The system behind Bitcoin is completely transparent and based on maths and the actual consensus of the everyday user. With all this in mind, what do you think? Which s a better option for our future? Bitcoin or fiat?
Are you ready to buy cryptocurrencies?
Get started nowThis article does not constitute investment advice, nor is it an offer or invitation to purchase any digital assets.
This article is for general purposes of information only and no representation or warranty, either expressed or implied, is made as to, and no reliance should be placed on, the fairness, accuracy, completeness or correctness of this article or opinions contained herein.
Some statements contained in this article may be of future expectations that are based on our current views and assumptions and involve uncertainties that could cause actual results, performance or events which differ from those statements.
None of the Bitpanda GmbH nor any of its affiliates, advisors or representatives shall have any liability whatsoever arising in connection with this article.
Please note that an investment in digital assets carries risks in addition to the opportunities described above.