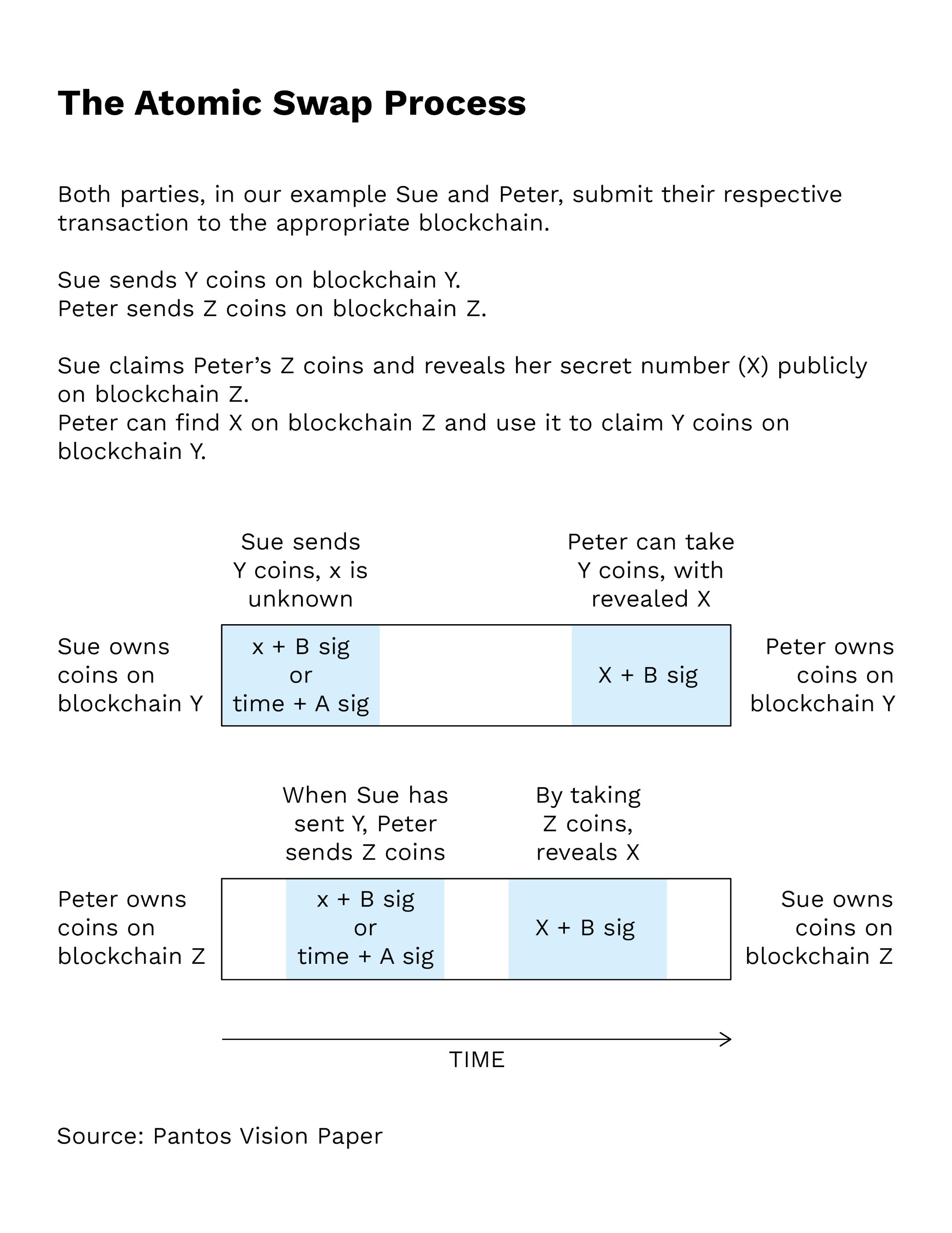
What is an atomic swap?
The original purpose of blockchain entails value transfers without the need for trusted third parties.
Limitations of blockchains extend past the issue of scalability
Atomic swaps offer a way to swap cryptocurrencies peer-to-peer from different blockchains directly
Timely execution of a Bitcoin transfer during an atomic swap is ensured by Hashed Timelock Contracts (HTLCs)
In this article, you will learn about the basics of atomic swaps.
Moving cryptocurrencies between blockchains
As the realm of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology is rapidly evolving with ever-increasing numbers of tokens, real-life use cases and functionalities, the actual interoperability between blockchains is still a cumbersome endeavour.
Limitations of many blockchains extend past the issue of scalability. Different use cases for blockchains mean different needs and standards in terms of network architecture and technology in a fractured blockchain space. This fragmentation prevents streamlining and hinders further development, while exposing blockchains to security vulnerabilities and ultimately slowing down adoption and the industry as a whole.
The case for swapping cryptocurrencies
All things considered, if you currently want to swap cryptocurrencies, it is a cumbersome endeavor. In any case, you need to log in to a cryptocurrency exchange, where the first issue may arise regarding the two cryptocurrencies you want to swap. Cryptocurrencies have fixed trading pairs which means that the pair of cryptocurrencies you want to trade against each other may not be available. Exchanges only have limited offers available. Preset combinations provided by the exchange of your choice mean that you, as a user, either have to live with the situation or opt for inconvenience through swapping across multiple currencies on various exchanges. There is also the potential for exchange downtimes and volume loss on top of barriers. This is where atomic swaps come in.
The basics of atomic swaps
Atomic swaps, also known as atomic cross-chain trading, offer a way to swap cryptocurrencies peer-to-peer from different blockchains directly without the requirement for a third party, such as an exchange.
Obviously such a swap has to take place in a set time frame, which - in Bitcoin - is ensured by a special type of smart contract called Hashed Timelock Contract (HTLC). A HTLC has an inbuilt timer ensures that the transaction is completed within the set timeframe. If the transaction is not executed within this time frame, it is automatically cancelled.
There are two types of atomic swaps: on-chain swaps between two different cryptocurrencies on two seperate blockchains, and off-chain swaps on second-layer channels off a main blockchain, such as the Lightning Network.
Since payments on the Lightning Network don’t require block confirmations or compete for space within blocks, they are convenient to use in environments where instant transaction speed is a high priority, such as in retail. They also help to pave the way of instant micropayments in the expanding space of internet-connected devices.
New to Bitpanda? Register your account today!
Sign up hereDespite their potential, atomic swaps have only been conducted with success using prototype systems with limited user-friendliness preventing mainstream adoption at this point. Furthermore, the concept behind conventional atomic swaps also comes with limitations. Additionally, basic user knowledge of coding is a must.
Also, atomic swaps in their current form are neither fast enough for mass adoption, nor do enough wallet providers allow the method, consequently forcing users to hold on to depreciating assets for lack of alternatives.
Projects such as Pantos, a multi-stakeholder open-source driven research project to enable decentralised cross-chain token transfers will be outlined in the Bitpanda Academy’s Expert section.
Are you ready to buy cryptocurrencies?
Get started nowDISCLAIMER
This article does not constitute investment advice, nor is it an offer or invitation to purchase any crypto assets.
This article is for general purposes of information only and no representation or warranty, either expressed or implied, is made as to, and no reliance should be placed on, the fairness, accuracy, completeness or correctness of this article or opinions contained herein.
Some statements contained in this article may be of future expectations that are based on our current views and assumptions and involve uncertainties that could cause actual results, performance or events which differ from those statements.
None of the Bitpanda GmbH nor any of its affiliates, advisors or representatives shall have any liability whatsoever arising in connection with this article.
Please note that an investment in crypto assets carries risks in addition to the opportunities described above.