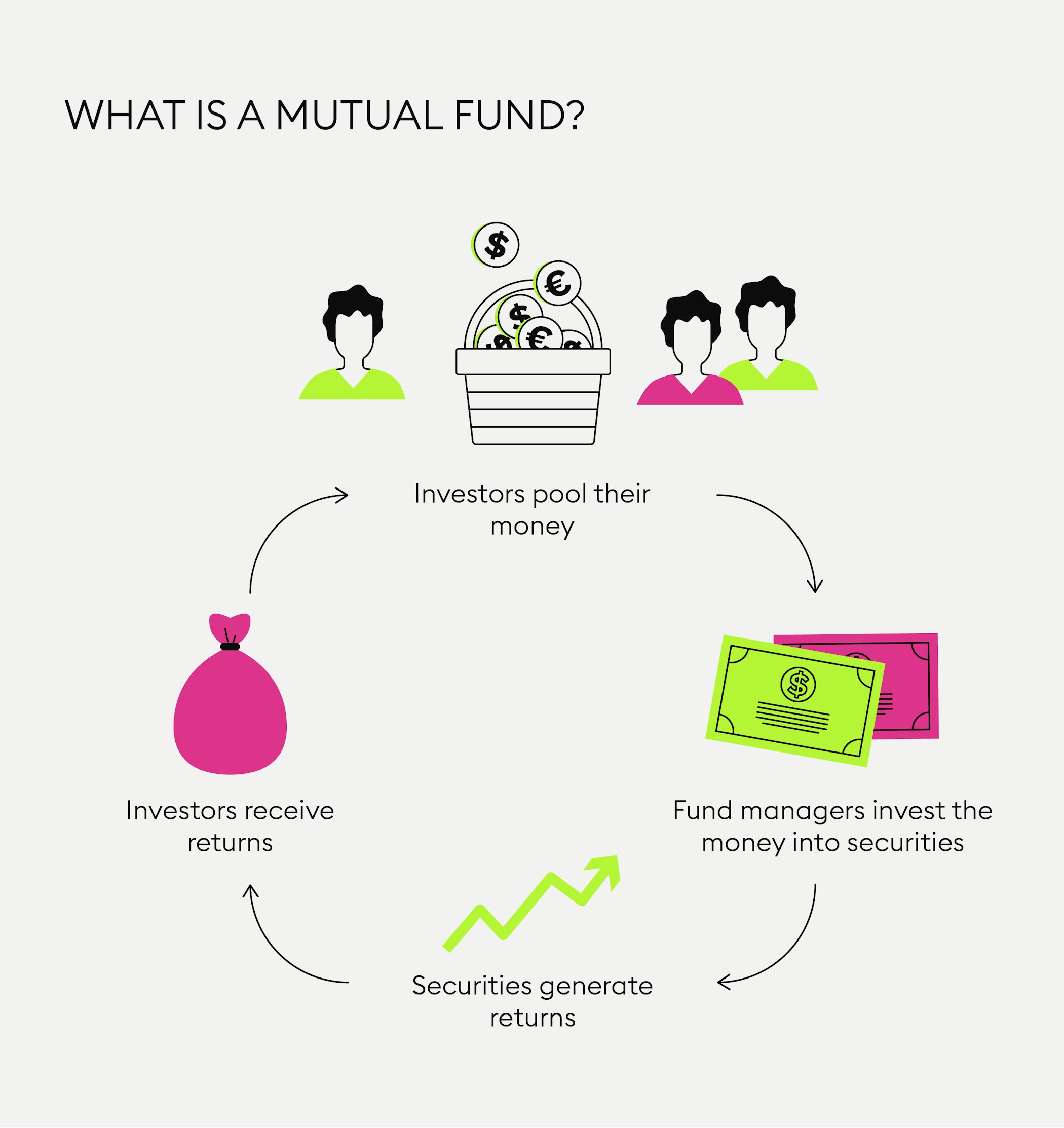
What is a mutual fund?
A mutual fund is a portfolio of stocks, bonds and various other types of securities managed by expert brokers. Investing in a fund instead of individual securities offers various advantages.
An investment fund consists of different securities that have been selected to meet the objective of the investment fund.
By placing investor money across different industries and companies, fund managers diversify in hopes of maximising profits while reducing risks.
Investors select funds to invest in based on criteria such as risks, objectives and fees and others.
What is a fund?
Generally speaking, a fund is money that you set aside for a specific purpose. An emergency fund is money that you set aside for emergencies. You may also have a retirement fund or other types of personal funds.
What is a mutual fund?
One of the most common types of investment funds is a “mutual fund”, an actively managed portfolio or pool of stocks, bonds and other assets that investors can buy shares in. In simple terms, it is an investment vehicle where many investors deposit money together by buying shares and therefore all co-own parts of the fund.
Unlike passive funds tied to an index, mutual funds are actively managed by capital investment companies. These companies act as brokers and select various securities based on risk parameters and the orientation of the fund.
Equity funds often manage over a hundred different individual stocks. As you can imagine, a private investor is usually unable to spread assets across such a wide range of stocks for financial reasons, so this is where investment funds come in.
A mutual fund is managed by investment professionals. It is usually an “open-end” or “open-ended fund”, meaning that shares can be purchased and also be returned to the issuing company by fund managers.
The size of a company based on its market capitalisation is an important factor in the structure of a mutual fund. Funds that are mainly invested in companies with large market capitalisation (“large caps”) have been known to pay steady dividends at low risk for the investor, while companies that are considered “mid-caps” may offer higher returns than large caps, albeit at higher risk and “small caps” are putting in strong growth while being highly volatile, meaning stock prices may fluctuate strongly.
What are index funds?
An investment fund may also be based on an index, meaning that a fund replicates the performance of a stock market index. In this case, the securities in this fund are the same as in the index. In this case we are speaking of a “passive fund”. Mutual funds require a high degree of active management by expert managers, which is why they are usually associated with higher costs for investors.
Thanks to such extensive diversification, the consequences of individual company defaults, like a company declaring bankruptcy, are usually much less significant when investing in a fund with many different assets.
New to Bitpanda? Register your account today!
Sign up hereWhat are the advantages and disadvantages of mutual funds?
Each investor acquires and holds shares and participates in the income generated by a large number of assets that make up the mutual fund. By placing investors’ money across securities in a broad range of companies in different industries, fund managers diversify in hopes of maximising profits and minimising risks. They monitor stock market performance and market developments and rebalance assets if necessary.
As a consequence of the extensive management involved in mutual funds, investors have to pay relatively high fees. Before you invest, you should do thorough research on which funds are suited to your needs. Don’t forget about the fees in relation to the amount you are planning on investing and taxation of gains.
In case of index funds, investors should also bear in mind that if a company falls out of an index, for instance because it is knocked out of the stock market index that the index fund is replicating, passive funds - which track a specific index or market segment - may suffer as a result.
Obviously, at such a time, many funds will simultaneously be selling the stock of a company leaving the index - and quick market players will do this even days before a fund is able to sell, thus significantly affecting the price.
All in all, the convenience and spread of risk and diversification behind mutual funds has been a decisive factor in making them increasingly popular investment vehicles for beginners and seasoned investors alike.
Which is a better investment option
DISCLAIMER
This article does not constitute investment advice, nor is it an offer or invitation to purchase any crypto assets.
This article is for general purposes of information only and no representation or warranty, either expressed or implied, is made as to, and no reliance should be placed on, the fairness, accuracy, completeness or correctness of this article or opinions contained herein.
Some statements contained in this article may be of future expectations that are based on our current views and assumptions and involve uncertainties that could cause actual results, performance or events which differ from those statements.
None of the Bitpanda GmbH nor any of its affiliates, advisors or representatives shall have any liability whatsoever arising in connection with this article.
Please note that an investment in crypto assets carries risks in addition to the opportunities described above.